-40%
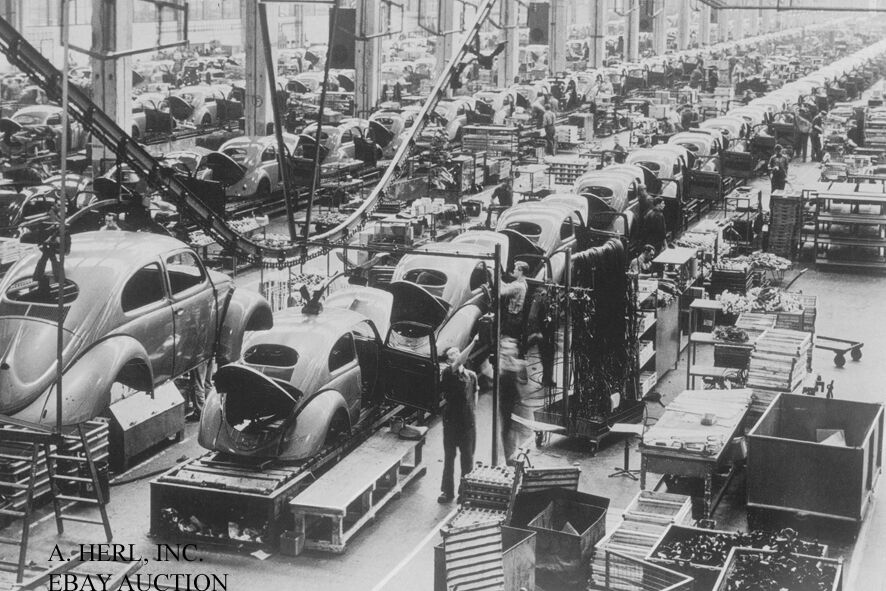
Volkswagen Beetle – VW Bug – VW Käfer – 1954 assembly in VW - photo photograph
$ 5.14
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
A superb and rare photo of thefinal assembly
in
1954
of the
Volkswagen Beetle
, officially called
Volkswagen Type 1
, and in
Germany
known as the
Volkswagen Käfer
(
VW Bug
in English).
The image shows the production process of one of the greatest cars ever made in the Wolfsburg VW factory.
The
Volkswagen Beetle
, officially known as the type 1, and originally called in German ‘Käfer’, is an economy car produced by the German auto maker Volkswagen (VW) from 1938 until 2003. Although the names "Beetle" and "Bug" were quickly adopted by the public, it was not until August 1967 that VW itself began using the name Beetle in marketing materials in the
US
. In most countries the Beetle is known as either the "Type I" or as the 1100, 1200, 1300, 1500, or 1600 which had been the names under which the vehicle was marketed in
Europe
; the numbers denoted the vehicle's approximate engine size in cubic centimetres. In 1998, many years after the original model had been dropped from the lineup in most of the world (production continued in
Mexico
until 2003), VW introduced the "New Beetle" (built on a Volkswagen Golf Mk4 platform) which bore a cosmetic resemblance to the original. Starting in 1931, Ferdinand Porsche and Zündapp developed the "Auto für Jedermann" (car for the everyman). This was the first time the name "Volkswagen" was used. Porsche already preferred the flat-4 cylinder engine, but Zündapp used a watercooled 5-cylinder radial engine. In 1932, three prototypes were running. All of those cars were lost during the war, the last in a bombing raid over
Stuttgart
in
1945. In
1933, Adolf Hitler gave the order to Ferdinand Porsche to develope a "Volks-Wagen" (the name means "people's car" in German, in which it is pronounced, a basic vehicle that should be capable of transporting two adults and three children at a speed of
100 km/h
(
62 mph
). The People's Car would be made available to citizens of the Third Reich through a savings scheme at 990 Reichsmark, about the price of a small motorcycle at the time (an average income being around 32RM/week). Erwin Komenda, Porsche's chief designer, was responsible for the design and styling of the car. Production only became financially viable, however, when it was backed by the Third Reich. War broke out before the large-scale production of the "People's Car" could commence, and manufacturing capacity was shifted to producing military vehicles. Production of civilian VW automobiles did not start until after the post-war occupation began. Initially called the Porsche 60 by Ferdinand Porsche, it was officially named the KdF-Wagen when the project was launched. The name refers to Kraft durch Freude (Strength Through Joy), the official leisure organization in the Third Reich. It was later known as the Type 1, but became more commonly known as the Beetle after World War II. Prototypes appeared from 1931 onwards. Much of the Beetle's design was inspired by the advanced Tatra cars of Hans Ledwinka, particularly the T97. This car also had a streamlined body and a rear-mounted 4 cylinder horizontally-opposed air-cooled engine. The Tatra V570, a prototype for a smaller car, also shows quite a resemblance to the later Volkswagens. Tatra launched a lawsuit, but this was stopped when
Germany
invaded
Czechoslovakia
. At the same time, Tatra was forced to stop producing the T97. The matter was re-opened after WW2 and in 1961 Volkswagen paid Tatra 3,000,000 Deutsche Marks in compensation. These damages meant that Volkswagen had little money for the development of new models and the Beetle's production life was necessarily extended. In occupied
Germany
, the Allies followed the Morgenthau plan to remove all German war potential by complete or partial pastoralization. As part of this, in the Industrial plans for
Germany
, the rules for which industry
Germany
was to be allowed to retain were set out. German car production was set at a maximum of 10% of the 1936 car production numbers. The Volkswagen factory at
Wolfsburg
was handed over by the Americans to British control in 1945; it was to be dismantled and shipped to
Britain
. Thankfully for Volkswagen, no British car manufacturer was interested in the factory; "the vehicle does not meet the fundamental technical requirement of a motor-car ... it is quite unattractive to the average buyer ... To build the car commercially would be a completely uneconomic enterprise." The factory survived by producing cars for the British Army instead. The re-opening of the factory is largely accredited to British Army officer Major Ivan Hirst (1916–2000). Hirst was ordered to take control of the heavily bombed factory, which the Americans had captured. His first task was to remove an unexploded bomb which had fallen through the roof and lodged itself between some pieces of irreplaceable production equipment; if the bomb had exploded, the Beetle's fate would have been sealed. Hirst persuaded the British military to order 20,000 of the cars, and by 1946 the factory was producing 1,000 cars a month. During this period the car and its town changed their Nazi-era names to Volkswagen (people's car) and
Wolfsburg
, respectively. The first 1,785 Beetles were made in a factory near
Wolfsburg
in 1945. Following the Army-led restart of production, Heinz Nordhoff was appointed director of the Volkswagen factory, under whom production increased dramatically over the following decade, with the one-millionth car coming off the assembly line by 1955. During this Post-war period, the Beetle had superior performance in its category with a top speed of
115 km/h
(
71 mph
) and 0-
100 km/h
(0-
60 mph
) in 27.5 seconds on 7.6 l/100 km (31mpg) for the standard 25 kilowatts (34 hp) engine. This was far superior to the Citroën 2CV and Morris Minor, and even competitive with more modern small cars like the Mini of the 1960s and later. The engine fired up immediately without a choke. It had tolerable road-handling and was economical to maintain. Although a small car, the engine has great elasticity and gave the feeling of better output than its small nominal size. During the 1950s, the car was modified progressively: the obvious visual changes mostly concerned the windows. In March 1953, the small oval two piece rear window was replaced by a slightly larger single piece oval rear window. More dramatically, in August
1957 a
much larger full width rear window replaced the oval one. 1964 saw the introduction of a widened cover for the light over the rear license plate. Towards the end of 1964, the height of the side windows and windscreen was slightly increased giving the cabin a less pinched look: this coincided with the introduction of a very slightly curved windscreen, though the curve was barely noticeable. The same body appeared during 1966, with a 1300 cc engine in place of the 1200 cc engine: it was only in the 1973 model Super Beetle that the beetle acquired an obviously curved windscreen. The flat windshield remained on the standard beetle. During the 1960s and early 1970s, innovative advertising campaigns and a reputation for reliability and sturdiness helped production figures to surpass the levels of the previous record holder, the Ford Model T, when Beetle No. 15,007,034 was produced on
17 February 1972
. By 1973, total production was over 16 million, and by
23 June 1992
, there had been over 21 million produced. In 1971, while production of the "standard" Beetle continued, a Type 1 variant called the Super Beetle, produced from model year 1971 to 1979 (1302s from 1971 to 1972, and 1303s from 1973 onwards), offered MacPherson strut front suspension, which required a significant redesign of the front end. This resulted not only in a better turning radius (despite having a
20 mm
(3/4 in) longer wheelbase), but because of the replacement of the bulky dual parallel torsion bar beams which had intruded upward into a large area within the trunk, and the stretched "nose" of the vehicle which permitted the relocation of the spare tire from a near vertical to a low horizontal position, this opened up approximately double the usable luggage space in the front compartment. 1972 Super Beetles had a slightly larger rear window, larger front brakes, and four rows of vents (vice two rows previously) on the engine deck lid. The tail lights now incorporated reversing lights. The "four spoke" steering wheel and steering column were re-enginneered to the "energy absorbing" design for better crash safety. A socket for the VW Dealer Diagnosis was fitted inside the engine compartment. In 1973, the introduction of a more aerodynamically curved windscreen pushed it forward and away from the passengers, purportedly due to US Department of Transportation safety requirements. This allowed for a redesigned, "padded" dashboard (all pre-73 Beetles had virtually no horizontal dash area). A 2-speed heater fan, higher rear mudguards, and larger tail lights (nicknamed 'elephant's feet') were added. The changes to the heater/windshield wiper housing and curved windshield resulted in slight redesign of the front hood, making the 1971 and 1972 Super Beetle hoods unique. For 1974 the previous flat steel bumper mounting brackets were replaced with tubular "self restoring energy absorbing" attachments, effectively shock absorbers for the bumpers. The steering knuckle and consequently the lower attach point of the strut was redesigned to improve handling and stability in the event of a tire blowout. This makes the struts from pre-74 Supers not interchangable with 1974-79 makes. 1975 brought the replacement of carburetors with Air Flow Control (AFC) Fuel Injection on
U. S.
and Canadian Beetles, a derivative of the more complex Bosch fuel injection system used in the Volkswagen Type III. The fuel injected engine also received a new muffler and the option of an upstream catalytic converter required on some models (e.g. California), necessitating a bulge in the rear apron sheet metal directly under the rear bumper, and replacing the distinctive dual "pea shooter" pipes with a single offset tailpipe, all of which make the fuel injected models easy to identify at a glance. Other changes were rack and pinion steering vs. the traditional worm and roller gearbox, and a larger license plate lamp housing below the engine lid. The front turn indicators were moved from the top of the fenders into the bumper bars on European models, a portend of the "Euro look" style years later by Beetle restorers. In 1976, the hard top Super Beetle and 1300 were discontinued (though convertibles remained Super Beetles through 1979) and replaced with an 'improved' standard Beetle with 1600 cc engine, IRS rear suspension, front disc brakes, blinkers in the front bumpers, elephant's foot tail lights and rubber inserts in the bumper bars. The "Auto-stick" transmission was dropped. 1976-on Super Beetles saw no significant engineering changes, only a few cosmetic touches and new paint options, including the "Champagne Edition" models (white on white was one example) to the final 1979 "Epiloge Edition" black on black, in salute to the first beetles ever produced from 1930s. Though extremely successful in the 1960s, the Beetle was faced with stiff competition from more modern designs. The over-reliance on the Beetle meant that Volkswagen was in financial crisis by 1974. It needed German government funding to produce the Beetle's replacement. Only when production lines at Wolfsburg switched to the new watercooled, front-engined, front-wheel drive Golf designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro in 1974, (sold in North America as the " Rabbit ") did Volkswagen produce a car as successful as the Beetle. The Golf would be periodically redesigned over its lifetime with only a few components carried over between models, while the Beetle used only minor refinements of its original design. The Golf did not kill Beetle production, which continued in smaller numbers at other German factories until
January 19, 1978
, when mainstream production shifted to
Brazil
and
Mexico
, markets where low operating cost was more important. It is important to note that the Beetle Cabriolet was still produced for the North American market in
Germany
until
January 10, 1980
. The last Beetle was produced in
Puebla
,
Mexico
, in mid-2003. The final batch of 3,000 Beetles were sold as 2004 models and badged as the Última Edición, with whitewall tires, a host of previously-discontinued chrome trim, and the choice of two special paint colors taken from the New Beetle. Production in
Brazil
ended in 1986, then restarted in 1993 and continued until 1996. Volkswagen sold Beetle sedans in the United States until August 1977 (the Beetle convertible a.k.a. Cabriolet was sold until January 1980) and in Europe until 1985, with private companies continuing to import cars produced in Mexico even after production of the beetle had ended. By 2002, over 21 million Type 1s had been produced. On
30 July 2003
, the last Type 1 rolled off the production line in
Puebla
,
Mexico
. It was car number 21,529,464, and was immediately shipped off to the company's museum in
Wolfsburg
,
Germany
. In true Mexican fashion, a big celebration and a mariachi band serenaded the last car in the 68-year-old history. The last car was nicknamed El Rey, which is Spanish for "The King", named after a legendary Mexican song by José Alfredo Jiménez. The last 3000 type 1s were called the "Última Edición" or the final edition.
Volkswagen
(abbreviated
VW
) is one of the world's largest automobile manufacturers. The company is headquartered in
Wolfsburg
, Lower Saxony, Germany. Volkswagen is the original marque within the Volkswagen Group, which includes the car marques Audi, Bentley Motors, Bugatti Automobiles, Automobili Lamborghini, SEAT, Škoda Auto and heavy goods vehicle manufacturer Scania. Volkswagen means "people's car" in German. Volkswagen was originally founded in
1937. In
the early 1930s German auto industry was still largely composed of luxury models, and the average German rarely could afford anything more than a motorcycle. Seeking a potential new market, some car makers began independent "peoples' car" projects - Mercedes' 170H, Adler's AutoBahn, Steyr 55, Hanomag 1,3L, among others. The trend was not new, as Béla Barényi is credited with having conceived the basic design in the middle 1920's. Josef Ganz developed the Standard Superior (going as far as advertising it as the "German Volkswagen"). Also, in
Czechoslovakia
, the Hans Ledwinka's penned Tatra T77, a very popular car amongst the German elite, was becoming smaller and more affordable at each revision. In 1933, with many of the above projects still in development or early stages of production, Adolf Hitler declared his intentions for a state-sponsored "Volkswagen" program. Hitler required a basic vehicle capable of transporting two adults and three children at
100 km/h
(
62 mph
). The "People's Car" would be available to citizens of the Third Reich through a savings scheme at 990 Reichsmark, about the price of a small motorcycle (an average income being around 32RM a week). Despite heavy lobbying in favour of one of the existing projects, Hitler chose to sponsor an all new, state owned factory. The engineer chosen for the task was Ferdinand Porsche. By then an already famed engineer, Porsche was the designer of the Mercedes 170H, and worked at Steyr for quite some time in the late 1920s. When he opened his own design studio he landed two separate "Auto für Jedermann" (car for everybody) projects with NSU and Zündapp, both motorcycle manufacturers. Neither project come to fruition, stalling at prototype phase, but the basic concept remained in Porsche's mind time enough, so on 22 June 1934, Dr. Ferdinand Porsche agreed to create the "People's Car". Changes included better fuel efficiency, reliability, ease of use, and economically efficient repairs and parts. The intention was that ordinary Europeans would buy the car by means of a savings scheme ("Fünf Mark die Woche musst Du sparen, willst Du im eigenen Wagen fahren" — "Five Marks a week you must save, If to drive your own car you crave"), which around 336,000 people eventually paid into. Volkswagen honoured its savings agreements in
West Germany
(but not in
East Germany
) after World War II. Prototypes of the car called the "KdF-Wagen" (German: Kraft durch Freude — "strength through joy"), appeared from 1936 onwards (the first cars had been produced in
Stuttgart
). The car already had its distinctive round shape and air-cooled, flat-four, rear-mounted engine. The VW car was just one of many KdF programs which included things such as tours and outings. The prefix Volks— ("People's") was not just applied to cars, but also to other products in
Europe
; the "Volksempfänger" radio receiver for instance. On
28 May 1937
, the Gesellschaft zur Vorbereitung des Deutschen Volkswagens mbH (sometimes abbreviated to Gezuvor) was established by the Deutsche Arbeitsfront. It was later renamed "Volkswagenwerk GmbH" on
16 September 1938
. Erwin Komenda, the longstanding Auto Union chief designer, developed the car body of the prototype, which was recognizably the Beetle known today. It was one of the first to be evolved with the aid of a wind tunnel, in use in
Germany
since the early 1920s. The building of the new factory started
26 May 1938
in the new town of
KdF-Stadt
, now called
Wolfsburg
, which had been purpose-built for the factory workers. This factory had only produced a handful of cars by the time war started in 1939. None was actually delivered to any holder of the completed saving stamp books, though one Type 1 Cabriolet was presented to Hitler on
20 April 1938
(his 49th birthday). War meant production changed to military vehicles, the Type 82 Kübelwagen ("Bucket car") utility vehicle (VW's most common wartime model), and the amphibious Schwimmwagen which were used to equip the German forces. The company owes its post-war existence largely to one man, British Army officer Major Ivan Hirst, REME. In April 1945, KdF-Stadt, and its heavily bombed factory were captured by the Americans, and subsequently handed over to the British, within whose occupation zone the town and factory fell. The factories were placed under the control of Oldham-born Hirst. At first, the plan was to use it for military vehicle maintenance. Since it had been used for military production, and had been in Hirst's words a "political animal" rather than a commercial enterprise, the equipment was in time intended to be salvaged as war reparations. Hirst painted one of the factory's cars green and demonstrated it to British Army headquarters. Short of light transport, in September 1945 the British Army was persuaded to place a vital order for 20,000. The first few hundred cars went to personnel from the occupying forces, and to the German Post Office. Some British Service personnel were allowed to take their VW Beetles back to the United Kingdom when they were demobilised, and one of the very first Beetles brought back in that way (UK registration number JLT 420) is still owned by Peter Colborne-Baber, the son of the original proprietor of the UK's first official Volkswagen Importer, Colborne Garages of Ripley, Surrey. By 1946 the factory was producing 1,000 cars a month, a remarkable feat considering it was still in disrepair. Owing to roof and window damage, rain stopped production and new vehicles were bartered for steel required for more production. The car, and its town changed their Second World War-era names to "Volkswagen", and "
Wolfsburg
" respectively, and production was increasing. It was still unclear what was to become of the factory. It was offered to representatives from the British, American and French motor industries. Famously, all rejected it. After an inspection of the plant, Sir William Rootes, head of the British Rootes Group, told Hirst the project would fail within two years, and that the car "is quite unattractive to the average motorcar buyer, is too ugly and too noisy … If you think you're going to build cars in this place, you're a bloody fool, young man". In an ironic twist of fate, Volkswagen would manufacture a locally built version of Rootes's Hillman Avenger in
Argentina
in the 1980s, long after Rootes had gone bankrupt at the hands of Chrysler in 1978—the Beetle outliving the Avenger by over 30 years. Ford representatives were equally critical: the car was "not worth a damn," according to Henry Ford II, the son of Edsel Ford, although he did reportedly look at the possibility of taking over the VW factory, but dismissed the idea as soon as he looked up Wolfsburg on the map and found it to be too close for comfort to the East German border. In
France
, Citroën started the 2CV on a similar marketing concept. Meanwhile, in
Italy
, the Fiat 500 "Topolino" was developed In Occupied Germany, the Allies followed the Morgenthau Plan, to remove all German war potential, by complete or partial pastoralisation. As part of this, in the Industrial plans for
Germany
, the rules for which industry
Germany
was to be allowed to retain were set out. German car production was set at a maximum of 10% of the 1936 car production numbers. As mentioned above, the Volkswagen factory at
Wolfsburg
came under British control in 1945; it was to be dismantled and shipped to
Britain
.
You can always contact us for more Volkswagen and other automotive photos!
This is a very nice and very rare photo that reflects a wonderful era of Volkswagen ‘s automotive history in a wonderful way. This is your rare chance to own this photo, therefore it is printed in a nice large format of ca. 8" x 12" (ca. 20 x
30 cm
).
It makes it perfectly suitable for framing.
Shipping costs will only be $ 7.00 regardless of how many photos you buy. For 5 or more photos, shipping is free!
(Note: A. Herl, Inc. does not appear on photo, for ebay purposes only)
No copyright expressed or implied. Sold as collectable item only. We are clearing out our archives that we have gathered from various sources.
All items always sent well protected in PVC clear files
and board backed envelopes.
We have photographs that came from professional collections and/or were bought from the original photographer or press studio! They are all of professional and excellent quality.
After many decades of professionally collecting photographs and posters we are clearing out our archives. They make the perfect gift and are perfectly suited for framing. They will look gorgeous unframed and will be a true asset nicely framed with a border. They are a gorgeous and great asset in every home, workshop, workplace, restaurant, bar or club!
First come - first served. And you can always contact us for your requests. Please ask any questions before the auction ends.